Diabetes
Understanding and addressing diabetes is essential for leading a long and healthy life.
We all want to feel strong, energized, and ready to conquer whatever life throws our way. But diabetes can throw a wrench in those plans. This chronic condition, if left unchecked, can steal your energy, slow you down, and sideline you from the activities you love.
Here’s the reality check
Diabetes is more common than you might think, it’s estimated that about one in seven American men have diabetes. Yet many remain unaware of the risks and symptoms. Statistics reveal that men are not only more likely to develop type 2 diabetes and get diabetes with lower BMIs, but are also at a higher risk of experiencing severe complications. But the good news? Taking charge of your health can make a big difference.
There are two main types of diabetes:
Type 2 Diabetes
This is the most common type, where your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use it effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps your body use sugar (glucose) for energy
Type 1 Diabetes:
This is an autoimmune disease where your body attacks the cells that produce insulin.
Risk Factors
Despite the devastating statistics, there’s hope because our fight with diabetes is in our control. It’s not easy but with managing weight, diet, and lifestyle habits, we can beat diabetes.
Age
The risk of developing diabetes increases with age, particularly for men over 45.
Obesity
Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, is a significant risk factor for diabetes.
Family History
A family history of diabetes increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of physical activity contributes to weight gain and insulin resistance.
Poor Diet
High consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and lack of fruits and vegetables can lead to diabetes
High Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
These conditions are often linked with diabetes and increase cardiovascular risk.
Symptoms
1. Frequent Urination: Increased urination is a result of excess glucose in the blood.
2. Excessive Thirst: The need to urinate frequently can lead to dehydration.
3. Extreme Hunger: Inability to use glucose effectively can cause intense hunger.
4. Weight Loss: Rapid: Unexplained weight loss despite eating more.
5. Fatigue: Lack of energy due to the body’s inability to use glucose properly.
6. Blurred Vision: High glucose levels can result in swelling of the eye lens.
7. Slow Healing Sores and Frequent Infections: Poor blood circulation and immune response can cause this.
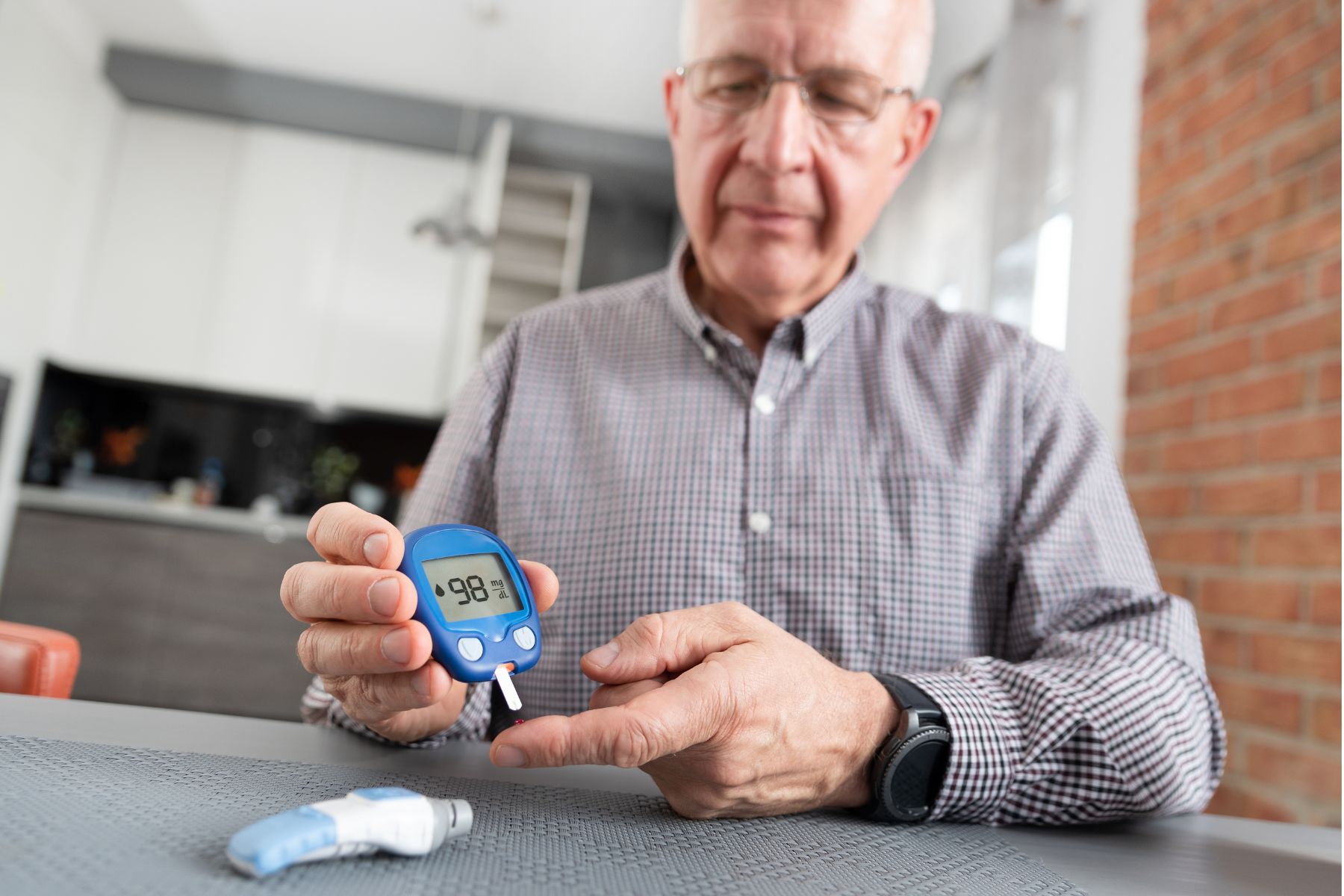
Screening and Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is crucial to managing and preventing complications associated with diabetes. Men should undergo regular screening, especially if they have risk factors such as obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, or a family history of diabetes. Common diagnostic tests include:
1. Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood sugar after an overnight fast.
2. A1C Test: Provides an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months.
3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: Measures blood sugar before and after consuming a sweet drink.
4. Random Blood Sugar Test: For those with severe symptoms; no preparation is required.
Treatment Options
Managing diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and monitoring. Treatment options include:
Lifestyle Modification
Medication
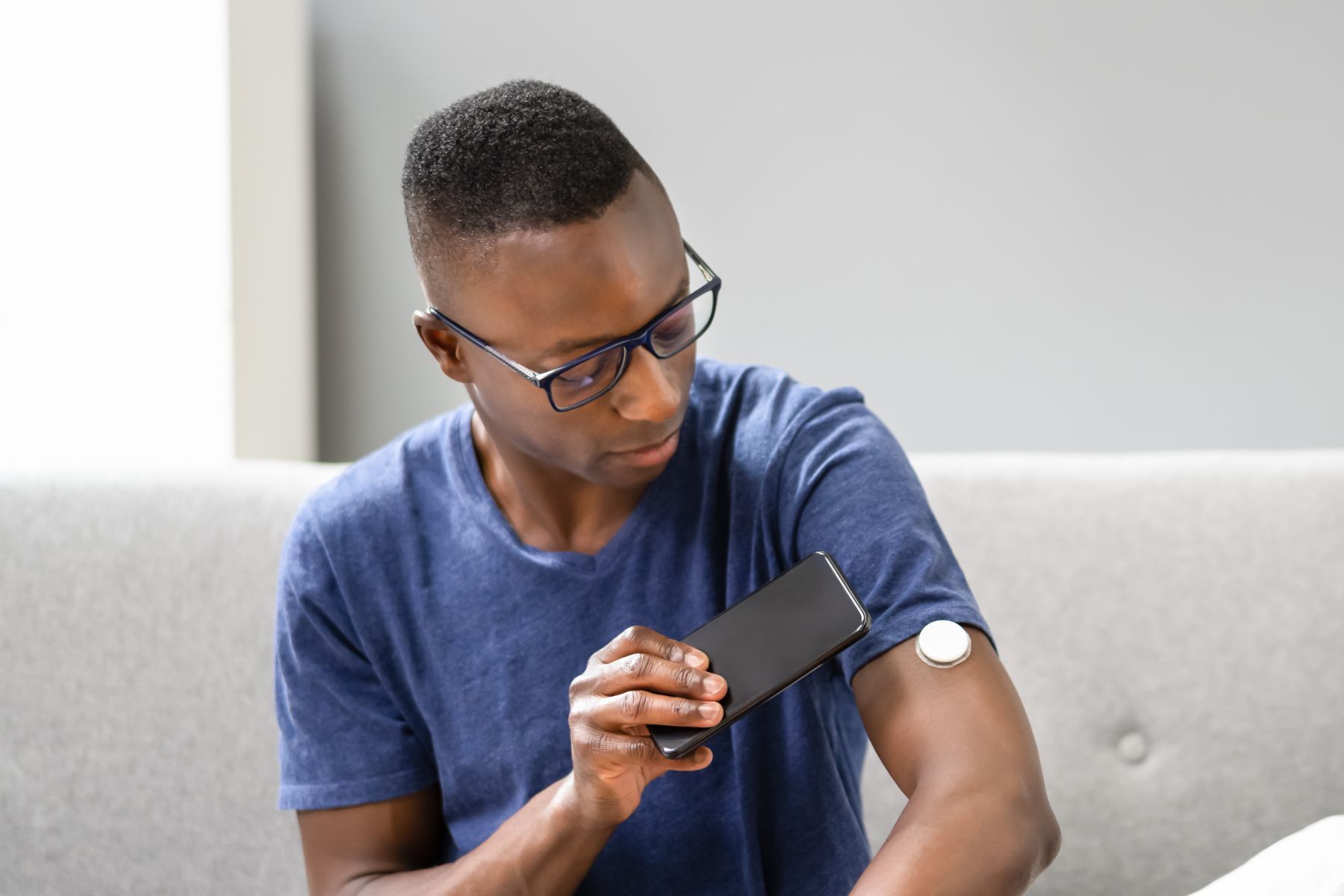
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Weight Management
How Men Can Minimize Their Risk
Men can take several proactive steps to reduce the risk of developing diabetes:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Aim for a BMI within the normal range by following a balanced diet and regular exercise regimen.
2. Get Active: Incorporate physical activity into your daily routine, take the stairs instead of the elevator, or go for a walk during lunch breaks.
3. Eat a Nutritious Diet: Focus on eating whole foods and reducing consumption of high-calorie, low-nutrient items.
4. Limit Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol can increase the risk of diabetes; moderate consumption is advised.
5. Avoid Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of diabetes and related complications.
6. Regular Health Check-ups: Routine visits to the doctor can catch warning signs early and monitor existing health conditions.
Where to Get Support
Living with diabetes can be challenging, but numerous resources and support networks are available to help men manage their condition effectively:
1. Men’s Health Network Newsletter: Sign up for our newsletter. It offers the latest information, resources, and support tailored to men’s health issues, including diabetes.
2. Diabetes Education Programs: Often available at hospitals and clinics, these programs provide valuable knowledge and skills for managing diabetes.
3. Support Groups: Engaging with others who have similar experiences can offer emotional support and practical tips. There are a number of online resources with listings of support groups tailored to your situation.
4. Healthcare Providers: Regular consultations with doctors, endocrinologists, and other healthcare professionals are important to stay ahead of diabetes risk.