Stroke
Strokes are a serious health concern that affect thousands of men every year.
High Cholesterol
High cholesterol can lead to the build-up of fatty deposits in your arteries, forming plaques that can restrict or block blood flow. According to the American Heart Association, men aged 20 and older should have their cholesterol levels checked every four to six years, or more frequently if they have risk factors associated with cardiovascular diseases. Monitoring and managing your cholesterol levels is essential to maintaining good health. This often includes a combination of dietary changes, physical activity, and possibly medications prescribed by your doctor to help keep your cholesterol at healthy levels.
Lifestyle Choices
Certain lifestyle choices can elevate your stroke risk. Smoking, for instance, damages blood vessels and raises blood pressure. Studies have shown that men who smoke are twice as likely to suffer a stroke as non-smokers. An unhealthy diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can also contribute to artery-clogging plaque. Lack of exercise increases the likelihood of high blood pressure, obesity, and diabetes, all of which are significant risk factors for stroke. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that men aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity each week.
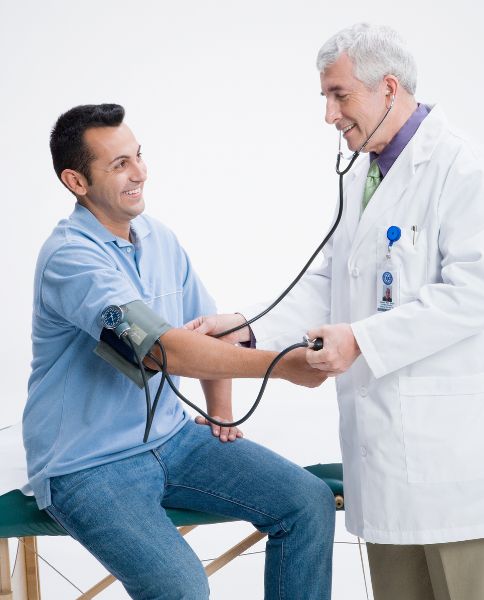
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is how hard the blood is pushing against the artery walls. Consistently high blood pressure can damage the arteries and make them more susceptible to clots and bursts, significantly increasing the risk of a stroke. Regular monitoring of your blood pressure and working with healthcare professionals to manage it through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes can be lifesaving.
Physical Exercise and Its Role in Prevention
Physical exercise is a cornerstone of stroke prevention. Regular physical activity helps to reduce blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and maintain a healthy weight. Men who engage in regular physical exercise are less likely to suffer from high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity, thereby reducing their stroke risk. The CDC recommends both aerobic and muscle-strengthening activities to maintain optimal men’s health
Mental Health Considerations
Mental health is often an overlooked aspect of stroke prevention. Depression, anxiety, and chronic stress can negatively affect cardiovascular health, elevating stroke risk. Ensuring mental well-being through activities such as mindfulness, counseling, and maintaining a strong social support network is imperative. Men often face unique challenges related to mental health, including societal pressure to appear strong and self-reliant, which can lead to underreporting of mental health issues and less seeking of help.
Dietary Changes
Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is key to lowering stroke risk. The Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, nuts, and fish, has been shown to reduce the risk of stroke. Limiting the intake of red meats, sugary snacks, and processed foods can also make a significant difference.
Regular Health Check-Ups
Incorporating regular check-ups with your healthcare provider helps in early identification and management of stroke risk factors. Healthcare professionals can provide personalized advice based on your health history and current condition, and they can monitor your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and glucose levels to ensure they meet healthy standards.